CRNN
CRNN是用来识别图片中的文字的简单来说就是对图片中的文字进行分类,先说一下大概过程,具体过程代码中
会详细记录实现.首先我们输入带有文字的图片,通过CNN得到特征,再进行维度变化,使其可以看成一个序列
这个序列会输入到RNN中进行计算,我们要将不固定的维度提出来这个不固定维度深层次表示了图片上的字数
集体是怎么做呢?
首先固定一个维度我们需要将图片高度固定,因为是一行一行识别,一行字高度需要固定,而一行几个字可以
先不确定,不固定这个我们可以理解为字数
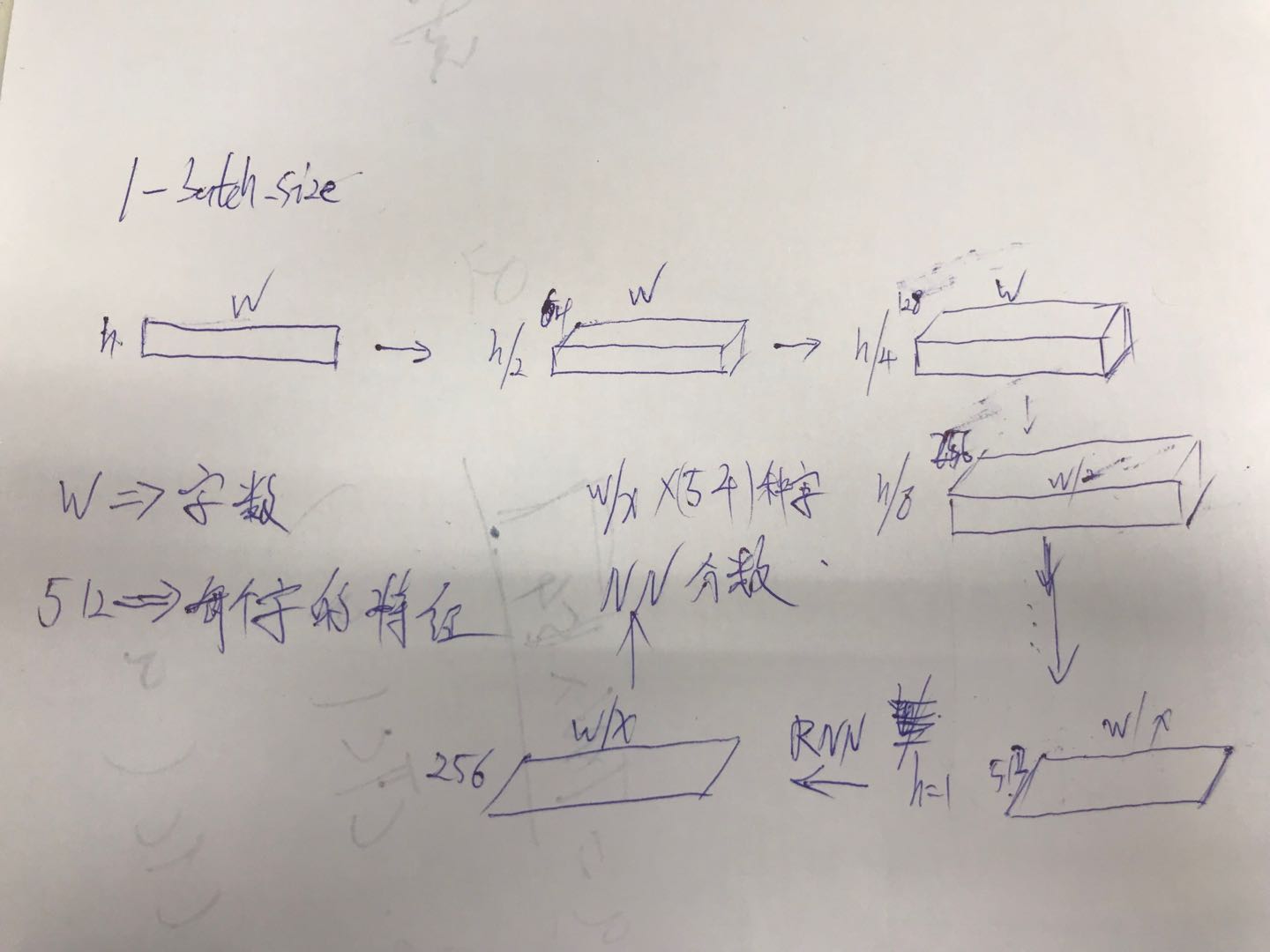 w维度上是不确定的字数,通过维度变化我们可以将这个维度挑出来当作待识别图片中的字数其他的所有参数
w维度上是不确定的字数,通过维度变化我们可以将这个维度挑出来当作待识别图片中的字数其他的所有参数
都可以固定, RNN后接一个全连接.
数据集
数据集是Synthetic_Chinese_String_Dataset,包含了中文的字和26字母大小写数字,标点符号等,在这个
数据集中有些生僻字我们不常见,这样导致模型作为分类器是有偏的.
数据集网上都能下载到.
label 27526484_437172851.jpg 178 934 1056 803 245 144 771 2100 378 40
号码表示对应字在词典中的位置

代码
在训练过程中使用CTC损失,ctc用的是pytorch自带的函数,百度出那个沙雕ctc真的是智障,各种环境配置
pytorch0.4前可以使用1.0后就不要用了.我使用出现的问题就是莫名其妙中断也不报错.使用gdb python
才能看出错误,出来的错误咱也不懂.
#参数设置
class DefaultConfig(object):
train_data_root = '/dataset/datasets/ocr/data_train.txt'
validation_data_root = '/dataset/datasets/ocr/data_test.txt'
modelpath = './mode.crnn'
image_path = '/dataset/datasets/ocr/Synthetic_Chinese_String_Dataset/'
batch_size = 64
img_h = 32
num_workers = 4
use_gpu = True
max_epoch = 10
learning_rate = 0.0005
weight_decay = 1e-4
printinterval = 200
valinterval = 1000
def parse(self,**kwargs):
for k,v in kwargs.items():
setattr(self,k,v)
DefaultConfig.parse = parse
opt = DefaultConfig()
import sys
import os
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES']='0'
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset,DataLoader
from torchvision import transforms as T
import cv2
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from warpctc_pytorch import CTCLoss #百度沙雕ctc
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import transforms
import collections
img_h=opt.img_h
batch_size=opt.batch_size
use_gpu=opt.use_gpu
max_epoch=opt.max_epoch
#读取词典
def readfile(filename):
res = []
with open(filename, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
for i in lines:
res.append(i.strip())
dic = {}
for i in res:
p = i.split(' ')
dic[p[0]] = p[1:]
return dic
#图像标准化
class resizeNormalize(object):
def __init__(self, size, interpolation=Image.BILINEAR):
self.size = size
self.interpolation = interpolation
self.toTensor = transforms.ToTensor()
def __call__(self, img):
img = img.resize(self.size, self.interpolation)
img = self.toTensor(img)
img.sub_(0.5).div_(0.5)
return img
#输入数据生成
class Chineseocr(Dataset):
def __init__(self, imageroot, labelroot):
self.image_dict = readfile(labelroot)
self.image_root = imageroot
self.image_name = [filename for filename, _ in self.image_dict.items()]
def __getitem__(self, index):
img_path = os.path.join(self.image_root, self.image_name[index])
keys = self.image_dict.get(self.image_name[index])
label = [int(x) for x in keys]
Data = Image.open(img_path).convert('L')
(w,h) = Data.size
size_h = 32
#高度变化为32
ratio = 32 / float(h)
size_w = int(w * ratio)
transform = resizeNormalize((size_w,size_h))
Data = transform(Data)
label=torch.IntTensor(label)
return Data,label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.image_name)
#实例化数据
train_data = Chineseocr(imageroot = opt.image_path,labelroot = opt.train_data_root)
train_loader = DataLoader(train_data,batch_size = opt.batch_size,shuffle = True)
val_data = Chineseocr(imageroot = opt.image_path,labelroot = opt.validation_data_root)
val_loader = DataLoader(val_data,batch_size = opt.batch_size,shuffle = True,num_workers = opt.num_workers)
#创建模型
class BidirectionalLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, nIn, nHidden, nOut):
super(BidirectionalLSTM, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(nIn, nHidden, bidirectional=True)
self.embedding = nn.Linear(nHidden * 2, nOut)
def forward(self, input):
recurrent, _ = self.rnn(input)
T, b, h = recurrent.size()
t_rec = recurrent.view(T * b, h)
output = self.embedding(t_rec) # [T * b, nOut]
output = output.view(T, b, -1)
return output
class CRNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, imgH, nc, nclass, nh, n_rnn=2, leakyRelu=False):
super(CRNN, self).__init__()
assert imgH % 16 == 0, 'imgH has to be a multiple of 16'
ks = [3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2]
ps = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0]
ss = [1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
nm = [64, 128, 256, 256, 512, 512, 512]
cnn = nn.Sequential()
def convRelu(i, batchNormalization=False):
nIn = nc if i == 0 else nm[i - 1]
nOut = nm[i]
cnn.add_module('conv{0}'.format(i),
nn.Conv2d(nIn, nOut, ks[i], ss[i], ps[i]))
if batchNormalization:
cnn.add_module('batchnorm{0}'.format(i), nn.BatchNorm2d(nOut))
if leakyRelu:
cnn.add_module('relu{0}'.format(i),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True))
else:
cnn.add_module('relu{0}'.format(i), nn.ReLU(True))
convRelu(0)
cnn.add_module('pooling{0}'.format(0), nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)) # 64x16x64
convRelu(1)
cnn.add_module('pooling{0}'.format(1), nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)) # 128x8x32
convRelu(2, True)
convRelu(3)
cnn.add_module('pooling{0}'.format(2),
nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2), (2, 1), (0, 1))) # 256x4x16
convRelu(4, True)
convRelu(5)
cnn.add_module('pooling{0}'.format(3),
nn.MaxPool2d((2, 2), (2, 1), (0, 1))) # 512x2x16
convRelu(6, True) # 512x1x16
self.cnn = cnn
self.rnn = nn.Sequential(
BidirectionalLSTM(512, nh, nh),
BidirectionalLSTM(nh, nh, nclass))
self.fc = FC(512,nclass)
def forward(self, input):
# conv features
conv = self.cnn(input)
b, c, h, w = conv.size()
assert h == 1, "the height of conv must be 1"
conv = conv.squeeze(2)
conv = conv.permute(2, 0, 1) # [w, b, c]
# rnn features
output = self.rnn(conv)
return output.log_softmax(2) #返回值这块我们需要更具实际情况考虑设定,pytorch的ctc需要输入log_softmax结果
#解码,就是去掉空和连续相同值保留一个
def decode(preds):
pred = []
for i in range(len(preds)):
if preds[i] != 0 and ((i == 0) or (i != 0 and preds[i] != preds[i-1])):
pred.append(int(preds[i]))
return pred
#读取字典
char_set = open('char_std_5990.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8').readlines()
char_set = ''.join([ch.strip('\n') for ch in char_set[1:]] + ['卍'])
n_class = len(char_set)
#验证效果,看准确率,就是一个批次每个字的准确率,
def val(net,loss_func,max_iter = 50):
print('start val')
net.eval()
totalloss = 0.0
k = 0
correct_num = 0
total_num = 0
val_iter = iter(val_loader)
max_iter = min(max_iter,len(val_loader))
for i in range(max_iter):
k = k + 1
(data,label) = val_iter.next()
labels = torch.IntTensor([])
for j in range(label.size(0)):
labels = torch.cat((labels,label[j]),0)
if torch.cuda.is_available and use_gpu:
data = data.cuda(cuda)
output = net(data)
output_size = torch.IntTensor([output.size(0)] * int(output.size(1)))
label_size = torch.IntTensor([label.size(1)] * int(label.size(0)))
loss = loss_func(output, labels, output_size, label_size) / label.size(0)
totalloss += float(loss)
pred_label = output.max(2)[1]
pred_label = pred_label.transpose(1,0).contiguous().view(-1)
pred = decode(pred_label)
total_num += len(pred)
for x,y in zip(pred,labels):
if int(x) == int(y):
correct_num += 1
accuracy = correct_num / float(total_num+0.000001) * 100
test_loss = totalloss / k
print('Test loss : %.3f , accuary : %.3f%%' % (test_loss , accuracy))
# 训练模型
cuda=2
model = CRNN(img_h, 1, n_class, 256)
if torch.cuda.is_available and use_gpu:
model.cuda(cuda)
learning_rate = opt.learning_rate
loss_func = nn.CTCLoss() #CTCLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate, weight_decay=opt.weight_decay)
k = 0
losstotal = 0.0
printinterval = opt.printinterval
valinterval = opt.valinterval
numinprint = 0
# train
for epoch in range(max_epoch):
print("第{}论".format(epoch))
for i,(data,label) in enumerate(train_loader):
#print("error1")
k = k + 1
numinprint = numinprint + 1
if torch.cuda.is_available and use_gpu:
data = data.cuda(cuda)
#print("error2")
loss_func = loss_func.cuda(cuda)
model.train()
labels = torch.IntTensor([])
for j in range(label.size(0)):
# print("error3")
labels = torch.cat((labels,label[j]),0)
#print("error4")
output = model(data)
# print("error5")
output_size = torch.IntTensor([output.size(0)] * int(output.size(1)))
label_size = torch.IntTensor([label.size(1)] * int(label.size(0)))
#print("error6")
loss = loss_func(output,labels,output_size,label_size) / label.size(0)
#print("error7")
losstotal += float(loss)
if k % printinterval == 0:
# display
print("[%d/%d] || [%d/%d] || Loss:%.3f" % (epoch,max_epoch,i + 1,len(train_loader),losstotal / numinprint))
losstotal = 0.0
numinprint = 0
torch.save(model.state_dict(), opt.modelpath)
writer.add_scalar('loss', loss, k)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if k % valinterval == 0:
# val
val(model,loss_func)